Generate spatial distribution objects for species, genera or families
Source:R/wcvp_distribution.R
wcvp_distribution.RdGenerate spatial distribution objects for species, genera or families
Usage
wcvp_distribution(
taxon,
taxon_rank = c("species", "genus", "family", "order", "higher"),
native = TRUE,
introduced = TRUE,
extinct = TRUE,
location_doubtful = TRUE,
wcvp_names = NULL,
wcvp_distributions = NULL
)Arguments
- taxon
Character. The taxon to be mapped. Must be provided.
- taxon_rank
Character. One of "species", "genus", "family", "order" or "higher", giving the rank of the value in
taxon.- native
Logical. Include native range? Defaults to
TRUE.- introduced
Logical. Include introduced range? Defaults to
TRUE.- extinct
Logical. Include extinct range? Defaults to
TRUE.- location_doubtful
Logical. Include occurrences that are thought to be doubtful? Defaults to
TRUE.- wcvp_names
A data frame of taxonomic names from WCVP version 7 or later. If
NULL(the default), names will be loaded fromrWCVPdata::wcvp_names.- wcvp_distributions
A data frame of distributions from WCVP version 7 or later. If
NULL(the default), distributions will be loaded fromrWCVPdata::wcvp_names.
Details
Where taxon_rank is higher than species, the distribution of the whole
group will be returned, not individual species within that group. This also applies when
toggling options - for example, introduced occurrences will only be included if they are
outside the native range, regardless of whether native=TRUE or native=FALSE.
To identify extinctions, introductions or doubtful occurrences within the native range,
the wcvp_summary and wcvp_occ_mat functions can be used.
Examples
# this example requires 'rWCVPdata'
if(requireNamespace("rWCVPdata")){
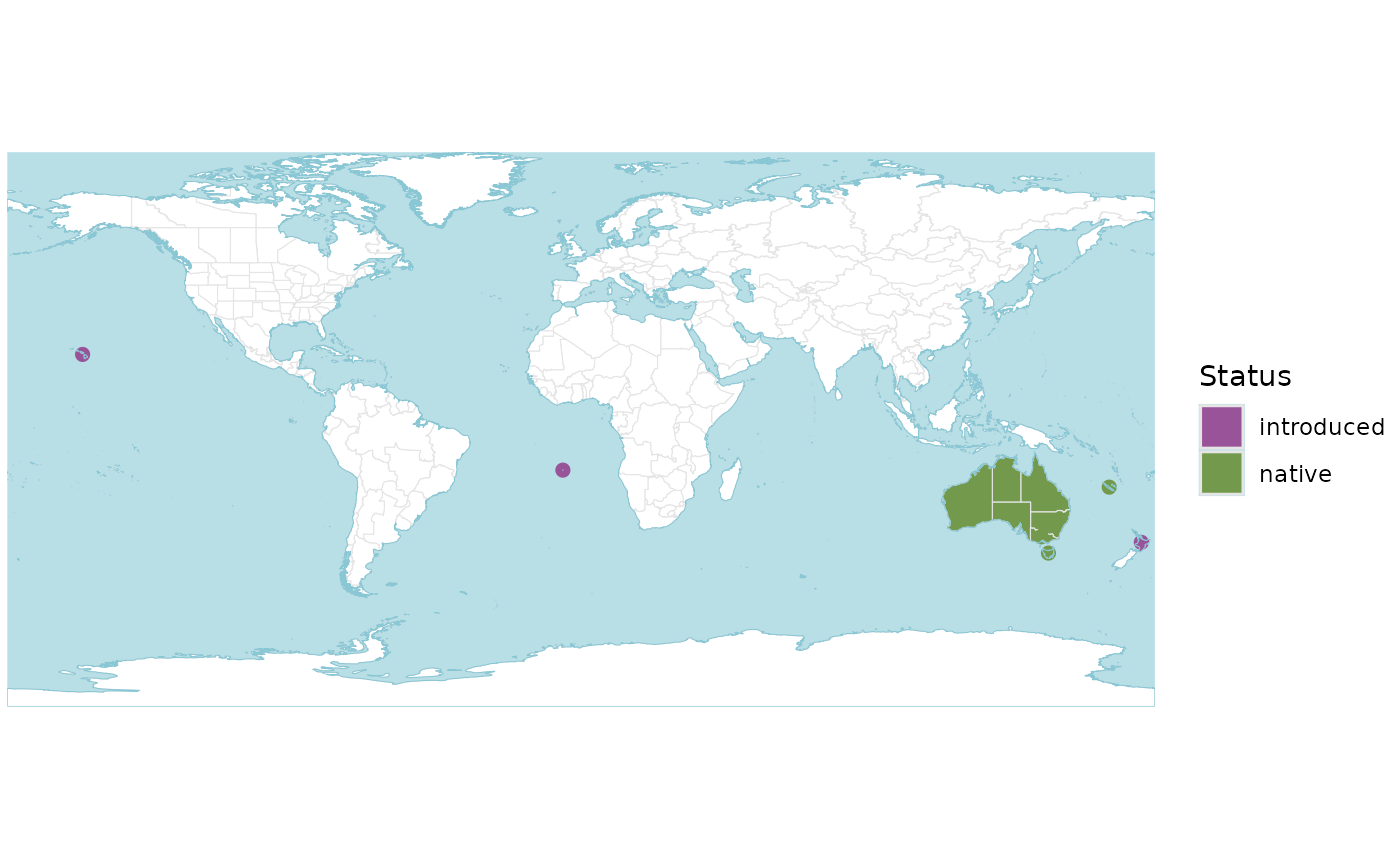
r <- wcvp_distribution("Callitris", taxon_rank = "genus")
p <- wcvp_distribution_map(r)
p
}
#> Warning: `aes_()` was deprecated in ggplot2 3.0.0.
#> ℹ Please use tidy evaluation idioms with `aes()`
#> ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the rWCVP package.
#> Please report the issue at <https://github.com/matildabrown/rWCVP/issues>.